Introduction to Go programming
Go, often referred to as Golang, is a programming language developed by Google. It was created by Robert Griesemer, Rob Pike, and Ken Thompson and was first announced in 2009. Go is designed to be a statically typed, compiled language with a focus on simplicity, readability, and efficiency.

Key features of Go include:
Concurrent programming: Go has built-in support for concurrent programming, making it easier to write programs that can efficiently perform tasks concurrently. This is achieved through goroutines (lightweight threads) and channels for communication between them.
Garbage collection: Go incorporates automatic garbage collection, which helps manage memory efficiently and eliminates the need for manual memory management.
Static typing: Go is statically typed, which means that variable types are known at compile time. This can help catch errors early in the development process and improve the performance of the compiled code.
Simplicity: Go is designed to be simple and straightforward, with a minimalistic syntax. It aims to reduce complexity and make the language easy to learn and read.
Fast compilation: Go programs are compiled quickly, allowing for rapid development and deployment of applications.
Cross-platform support: Go supports cross-compilation, making it easy to build binaries for different operating systems and architectures from a single codebase.
Standard library: Go comes with a rich standard library that includes packages for various common tasks, simplifying the development process.
Open source: Go is an open-source programming language, and its development is guided by the Go community. The source code is available for anyone to inspect, modify, and contribute to.
Go is often used in the development of web servers, networking tools, container orchestration systems (such as Kubernetes), and other distributed systems. It has gained popularity for its simplicity, efficiency, and suitability for building scalable and concurrent applications.



Project you could work on using the Go programming
Real-time Chat Application with WebSockets:
Create a real-time chat application using Go and WebSocket. This project will involve both server-side and client-side development.
1. Server-side (Go):
- Use the Gorilla WebSocket library in Go to handle WebSocket connections.
- Implement user authentication for the chat application.
- Create a simple chat room system where users can join different rooms.
- Implement features like broadcasting messages to all users in a room and handling private messages between users.
2. Client-side (HTML, CSS, JavaScript):
- Design a user-friendly interface for the chat application.
- Use HTML and CSS for the layout and styling.
- Use JavaScript to handle WebSocket connections from the client side.
- Allow users to choose a username, join different chat rooms, and send/receive messages in real-time.
3. Additional Features:
- Add support for emojis and file sharing in the chat.
- Implement notifications for new messages or mentions.
- Provide a history of messages for users who join a chat room.
- Implement basic moderation features, such as the ability for moderators to kick or ban users.
4. Deployment:
- Deploy the application on a cloud platform like AWS, GCP, or Heroku.
- Consider using Docker for containerization to simplify deployment.
Building a real-time chat application will allow you to explore WebSocket communication, user authentication, and both server-side and client-side development. It’s a practical project that involves various aspects of web development and can be expanded with additional features and improvements over time.
Key Features of the Go Programming
Go, commonly known as Golang, is a programming language developed by Google that has gained significant popularity for its simplicity, efficiency, and concurrency support. In this article, we’ll delve into some of the key features that make Go a compelling choice for developers.
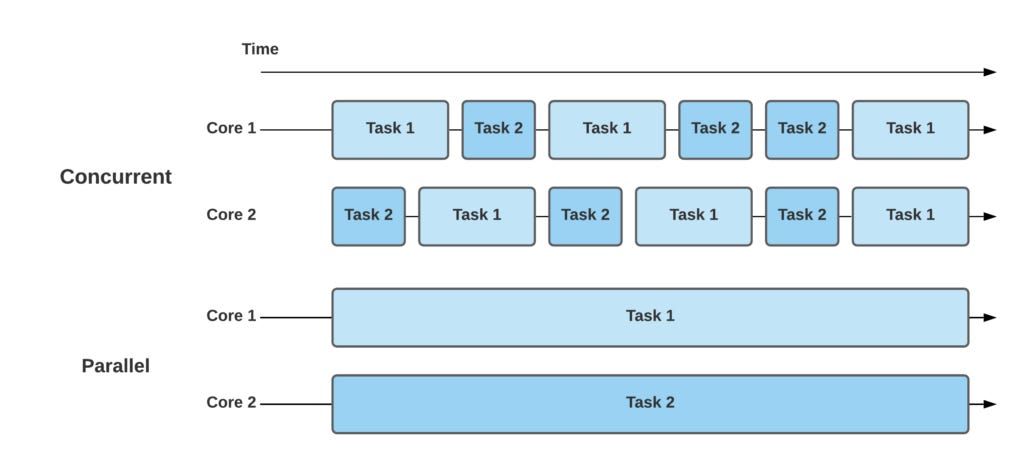
- Concurrent Programming: One standout feature of Go is its built-in support for concurrent programming. Go introduces the concept of goroutines, which are lightweight threads managed by the Go runtime. Goroutines make it easy to write concurrent code, enabling developers to efficiently execute multiple tasks concurrently without the complexities often associated with traditional threading models.
go func() {
// Concurrent task
}()Additionally, Go includes channels, a powerful mechanism for communication and synchronization between goroutines. This facilitates the development of concurrent and parallel applications with ease.
- Static Typing: Go is a statically typed language, meaning that variable types are known at compile time. This helps catch errors early in the development process, improving code reliability and maintainability. Despite its static nature, Go’s type system is designed to be expressive and flexible, allowing developers to write clean and concise code.
var age int
age = 25- Garbage Collection: Memory management is a critical aspect of programming, and Go addresses it through automatic garbage collection. Developers don’t need to explicitly manage memory allocation and deallocation, as the Go runtime takes care of this automatically. This feature reduces the risk of memory leaks and enhances the overall robustness of Go applications.
- Simplicity: Go is renowned for its simplicity and readability. The language is designed with a minimalistic syntax that avoids unnecessary complexity. This simplicity not only makes Go easy to learn for new developers but also enhances collaboration and code maintenance within development teams.
package main
import "fmt"
func main() {
fmt.Println("Hello, World!")
}- Fast Compilation: Go boasts fast compilation times, allowing developers to iterate quickly during the development process. This is particularly advantageous for large codebases and projects with frequent code changes. The quick compilation times contribute to a more efficient development workflow.
- Cross-Platform Support: Go supports cross-compilation, enabling developers to build binaries for various operating systems and architectures from a single codebase. This feature simplifies the deployment process and makes it easier to create applications that run seamlessly across different platforms.
- Standard Library: Go comes with a rich standard library that covers a wide range of functionalities. This eliminates the need for third-party libraries in many cases, as developers can leverage the standard library for tasks such as networking, file I/O, and more. The inclusion of a robust standard library enhances productivity and promotes best practices.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the Go programming language offers a unique combination of simplicity, concurrency support, and performance. Its features cater to the needs of modern developers, making it well-suited for a variety of applications, from web development to system programming. Whether you are a seasoned developer or a newcomer to the programming world, exploring Go can be a rewarding experience, opening doors to efficient and scalable software development.