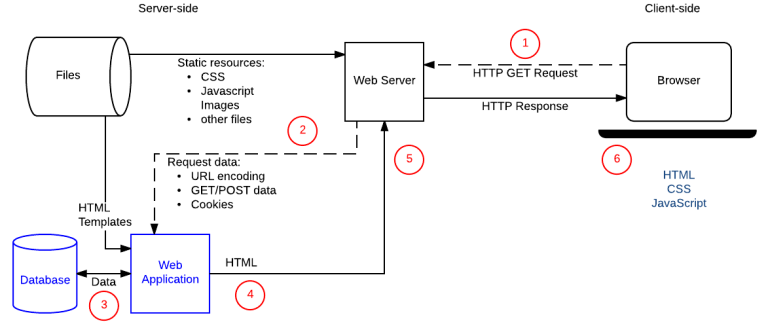
Introduction
Firebase, a comprehensive mobile and web application development platform provided by Google, offers a wide array of services to simplify backend development. Integrating Firebase with C# allows developers to leverage cloud-based features, such as real-time databases, authentication, cloud functions, and more. In this article, we’ll explore how to integrate C# with Firebase and tap into the capabilities it offers.
Setting Up Firebase Project
Before diving into C# integration, create a Firebase project and configure the necessary services. Follow these steps:
- Create a Firebase Project:
- Go to the Firebase Console.
- Click on “Add Project” and follow the setup instructions.
- Enable Services:
- In your Firebase project, enable the services you plan to use. For example, enable the Firebase Realtime Database, Authentication, or Cloud Firestore.
- Get Firebase Configuration:
- Navigate to Project Settings.
- In the General tab, find your project configuration, including the Firebase SDK snippet.
Now that your Firebase project is set up, let’s explore integrating it with C#.
Using Firebase SDK for C
Firebase provides an official SDK for C# developers to interact with its services seamlessly. Install the Firebase SDK using the NuGet Package Manager or Package Manager Console:
Install-Package Firebase.Database
This package includes C# bindings for Firebase Realtime Database.
Connecting to Firebase Realtime Database
Let’s create a simple C# console application that connects to the Firebase Realtime Database and performs basic operations.
using System;
using Firebase.Database;
using Firebase.Database.Query;
class Program
{
static async System.Threading.Tasks.Task Main(string[] args)
{
var firebaseClient = new FirebaseClient("YOUR_FIREBASE_DATABASE_URL");
// Writing data to the database
await firebaseClient.Child("messages").PostAsync(new Message { Content = "Hello, Firebase!" });
// Reading data from the database
var messages = await firebaseClient.Child("messages").OnceAsync<Message>();
foreach (var message in messages)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Message: {message.Object.Content}");
}
}
public class Message
{
public string Content { get; set; }
}
}Make sure to replace "YOUR_FIREBASE_DATABASE_URL" with the actual URL of your Firebase Realtime Database.
In this example, the program writes a message to the “messages” node and then reads and prints all messages from the same node.
Firebase Authentication with C
Firebase Authentication allows users to sign in to your application using various providers such as email/password, Google, Facebook, etc.
Let’s modify our C# program to include Firebase Authentication.
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Firebase.Auth;
class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
var authProvider = new FirebaseAuthProvider(new FirebaseConfig("YOUR_API_KEY"));
// Sign up a new user
var authResult = await authProvider.CreateUserWithEmailAndPasswordAsync("[email protected]", "password");
Console.WriteLine($"User created with ID: {authResult.User.LocalId}");
// Sign in
var signInResult = await authProvider.SignInWithEmailAndPasswordAsync("[email protected]", "password");
Console.WriteLine($"User signed in with ID: {signInResult.User.LocalId}");
// Sign out
authProvider.SignOut();
Console.WriteLine("User signed out.");
}
}Replace "YOUR_API_KEY" with your Firebase project’s API key.
This example demonstrates creating a new user account, signing in, and signing out using Firebase Authentication.
Firebase Cloud Functions with C
Firebase Cloud Functions enable serverless computing, allowing you to run backend code in response to events. Although Cloud Functions are typically written in Node.js, you can invoke them from your C# code.
Consider a C# console application that triggers a Cloud Function.
using System;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
class Program
{
static async Task Main(string[] args)
{
var functionUrl = "YOUR_CLOUD_FUNCTION_URL";
var httpClient = new HttpClient();
var response = await httpClient.PostAsync(functionUrl, null);
var result = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
Console.WriteLine($"Cloud Function Response: {result}");
}
}Replace "YOUR_CLOUD_FUNCTION_URL" with the actual URL of your Cloud Function.
This program sends an HTTP POST request to invoke the Cloud Function and prints the response.
Conclusion
Integrating C# with Firebase opens up a world of possibilities for building scalable, real-time, and feature-rich applications. Whether you’re working with Firebase Realtime Database, Authentication, Cloud Functions, or other Firebase services, the Firebase SDK for C# provides a seamless bridge between your C# code and the power of Google’s cloud platform.
As you explore these capabilities, refer to the Firebase documentation for detailed information and examples. With the right combination of C# and Firebase, you can create robust, dynamic, and secure applications that leverage the strengths of both technologies.