Certainly! Here are articles on different aspects of working with APIs in Python:
Introduction to Python APIs: What You Need to Know
- An overview of what APIs (Application Programming Interfaces) are, their importance, and how Python is commonly used to interact with them.
Making HTTP Requests in Python: A Beginner’s Guide
- Exploring the
requestslibrary to perform HTTP requests in Python, covering GET, POST, and handling response data.
Parsing JSON in Python: Working with API Responses
- A guide on how to parse JSON data returned from APIs using Python’s built-in
jsonmodule.
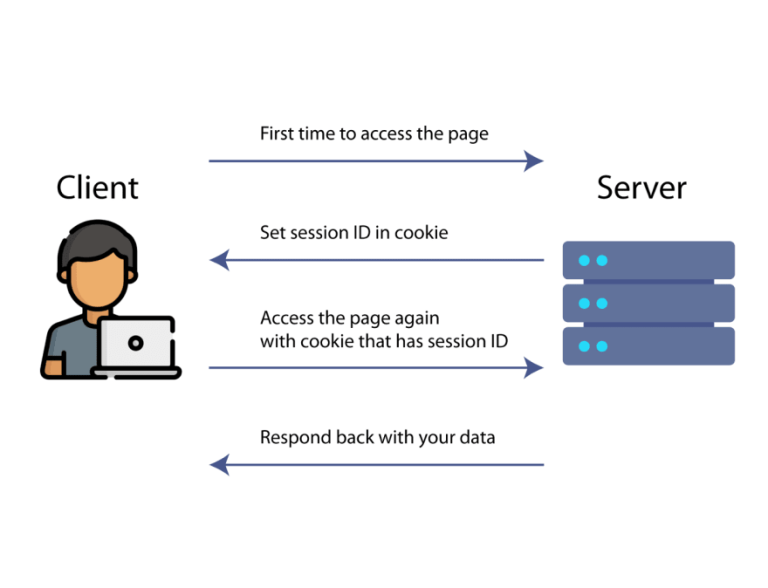
Authentication in Python APIs: Key Concepts and Methods
- Discussing various authentication methods such as API keys, OAuth, and token-based authentication when interacting with APIs using Python.
RESTful APIs with Flask: Building Your Own API
- A hands-on tutorial on creating a RESTful API using the Flask framework in Python, including defining routes, handling requests, and serving JSON responses.
Consuming RESTful APIs with Python: Best Practices
- Exploring best practices when consuming external RESTful APIs, covering error handling, rate limiting, and handling authentication securely.
GraphQL in Python: A Modern Approach to API Queries
- Introducing GraphQL and demonstrating how to use Python libraries like
grapheneto work with GraphQL APIs.
Working with APIs in Jupyter Notebooks: Data Retrieval and Analysis
- Showing how to leverage APIs within Jupyter Notebooks for data retrieval and analysis, using libraries like
pandasfor data manipulation.
Asynchronous API Requests in Python: Boosting Performance
- Exploring asynchronous programming with Python’s
asyncioandhttpxto make asynchronous API requests, improving efficiency in handling multiple requests.
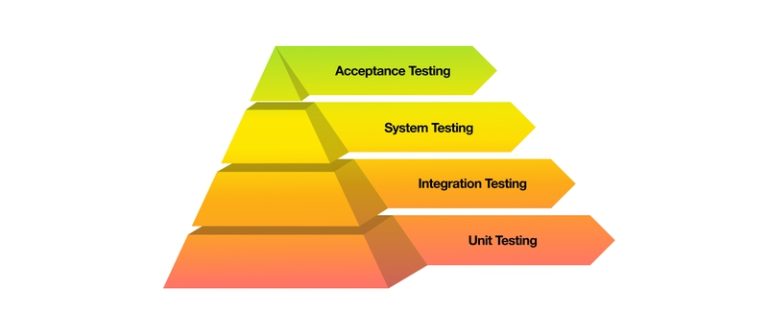
API Testing in Python: Strategies and Tools
- An overview of testing strategies for APIs, introducing tools like
unittestandpytestfor testing API endpoints in Python.

Here are sample codes for some of the concepts mentioned in the articles:
- Making HTTP Requests in Python:
import requests
response = requests.get('https://api.example.com/data')
print(response.status_code)
print(response.json()) # Assuming the response is in JSON format- RESTful APIs with Flask:
from flask import Flask, jsonify
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/api/data', methods=['GET'])
def get_data():
data = {"message": "Hello, this is your API response!"}
return jsonify(data)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(debug=True)- Consuming RESTful APIs with Python:
import requests
url = 'https://api.example.com/data'
headers = {'Authorization': 'Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN'}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
print(data)
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code}")- GraphQL in Python:
from gql import gql, Client
from gql.transport.requests import RequestsHTTPTransport
url = "https://api.example.com/graphql"
transport = RequestsHTTPTransport(url=url, verify=True, retries=3)
client = Client(transport=transport, fetch_schema_from_transport=True)
query = gql('''
query {
user(id: 1) {
username
email
}
}
''')
result = client.execute(query)
print(result)- Asynchronous API Requests in Python:
import asyncio
import httpx
async def fetch_data(url):
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
response = await client.get(url)
return response.text
async def main():
url = 'https://api.example.com/data'
result = await fetch_data(url)
print(result)
asyncio.run(main())Certainly! Here are sample codes for the concepts mentioned in articles 6 to 10:
- Consuming RESTful APIs with Python – Best Practices:
import requests
url = 'https://api.example.com/data'
headers = {
'Authorization': 'Bearer YOUR_ACCESS_TOKEN',
'User-Agent': 'YourApp/1.0'
}
try:
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=5)
response.raise_for_status()
data = response.json()
print(data)
except requests.exceptions.RequestException as err:
print(f"Error: {err}")- GraphQL in Python:
from gql import gql, Client
from gql.transport.requests import RequestsHTTPTransport
url = "https://api.example.com/graphql"
transport = RequestsHTTPTransport(url=url, verify=True, retries=3)
client = Client(transport=transport, fetch_schema_from_transport=True)
mutation = gql('''
mutation {
createUser(input: {username: "example", password: "secret"}) {
user {
id
username
}
}
}
''')
result = client.execute(mutation)
print(result)- Working with APIs in Jupyter Notebooks:
import requests
import pandas as pd
url = 'https://api.example.com/data'
response = requests.get(url)
if response.status_code == 200:
data = response.json()
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df.head())
else:
print(f"Error: {response.status_code}")- Asynchronous API Requests in Python:
import asyncio
import httpx
async def fetch_data(url):
async with httpx.AsyncClient() as client:
response = await client.get(url)
return response.text
async def main():
urls = ['https://api.example.com/data1', 'https://api.example.com/data2']
tasks = [fetch_data(url) for url in urls]
results = await asyncio.gather(*tasks)
for result in results:
print(result)
asyncio.run(main())- API Testing in Python:
import unittest
import requests
class APITestCase(unittest.TestCase):
def test_api_endpoint(self):
url = 'https://api.example.com/data'
response = requests.get(url)
self.assertEqual(response.status_code, 200)
# Add more assertions based on the expected API response
if __name__ == '__main__':
unittest.main()
These codes cover aspects like error handling, GraphQL mutations, working with data in Jupyter Notebooks, asynchronous requests, and API testing. If you have specific questions or need further clarification, feel free to ask!
These articles cover a range of topics related to working with APIs in Python, from making simple HTTP requests to building and testing your own APIs. If you have specific questions or want more details on any particular aspect, feel free to ask!