Introduction
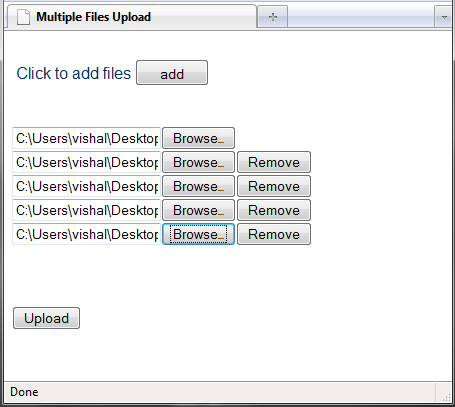
Uploading multiple files is a common requirement in web applications. In this article, we’ll explore how to achieve this in Python without using a web framework. We’ll build a simple script using the standard library’s http.server module to handle file uploads.
1. Understanding the Basics:
- Before diving into code, it’s crucial to understand the basics of file uploads over HTTP. When a client uploads files, the server receives the files as part of the HTTP request, typically using the
multipart/form-dataencoding.
2. Creating the HTML Form:
- Start by creating a basic HTML form that allows users to select and upload multiple files. The form should use the
enctype="multipart/form-data"attribute to enable file uploads.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>File Upload</title>
</head>
<body>
<form action="http://localhost:8000/upload" method="post" enctype="multipart/form-data">
<input type="file" name="files" multiple>
<input type="submit" value="Upload">
</form>
</body>
</html>3. Handling File Uploads in Python:
- Use the
http.servermodule, which is part of the Python standard library, to handle file uploads. Create a custom handler by subclassinghttp.server.BaseHTTPRequestHandler.
from http.server import HTTPServer, BaseHTTPRequestHandler
class FileUploadHandler(BaseHTTPRequestHandler):
def do_POST(self):
content_type, _ = cgi.parse_header(self.headers['content-type'])
if content_type == 'multipart/form-data':
form_data = cgi.FieldStorage(
fp=self.rfile,
headers=self.headers,
environ={'REQUEST_METHOD': 'POST'}
)
files = form_data.getlist('files')
for file in files:
# Save each file to the server or process as needed
with open(file.filename, 'wb') as f:
f.write(file.file.read())
self.send_response(200)
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(b'Successfully uploaded files')
else:
self.send_response(400)
self.end_headers()
self.wfile.write(b'Invalid content type')
def run(server_class=HTTPServer, handler_class=FileUploadHandler, port=8000):
server_address = ('', port)
httpd = server_class(server_address, handler_class)
print(f'Starting server on port {port}')
httpd.serve_forever()
if __name__ == '__main__':
run()4. Running the Server:
- Save the Python script, let’s call it
file_upload.py, and run it in your terminal. This will start a simple server athttp://localhost:8000.
python file_upload.py
5. Testing the File Upload:
- Open a web browser and navigate to
http://localhost:8000. You should see the file upload form. Select multiple files and click the “Upload” button. The server should respond with a success message.
6. Enhancements and Considerations:
- Depending on your use case, you may want to enhance the script by adding error handling, implementing file type checks, and securing the upload endpoint.
Conclusion:
- Uploading multiple files without a web framework in Python is achievable using the standard library’s
http.servermodule. While this approach is suitable for small projects or learning purposes, for production applications, consider using a web framework for more features, security, and scalability.