Introduction
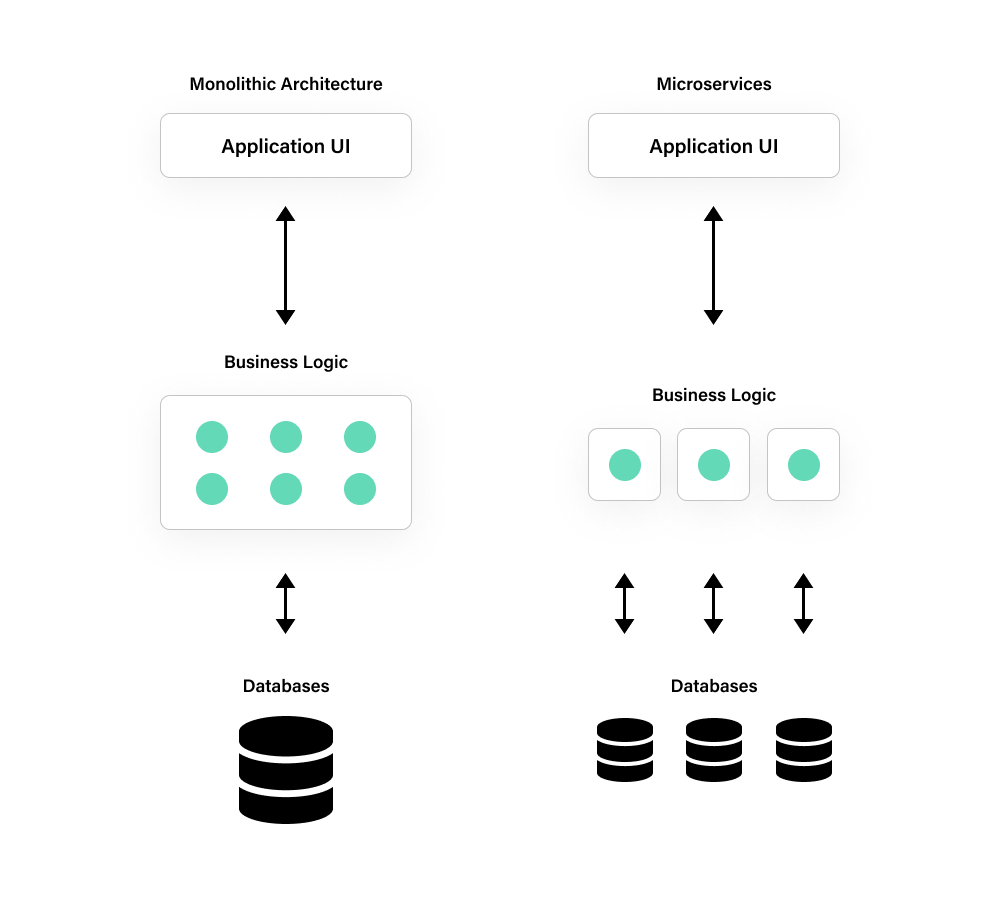
Microservices architecture has gained significant traction in the world of software development due to its scalability, flexibility, and ability to foster rapid innovation. Node.js, with its non-blocking I/O and event-driven architecture, is well-suited for building microservices. In this article, we’ll explore how to implement microservices using the top Node.js frameworks: Express.js, Koa.js, Nest.js, Sails.js, and Adonis.js.
1. Microservices with Express.js
Express.js, being a minimalist and flexible framework, is widely used for building microservices. Each microservice can be a standalone Express application, communicating with others through well-defined APIs. Here’s a simple example:
// Microservice 1
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const port = 3001;
app.get('/service1', (req, res) => {
res.json({ message: 'Microservice 1 response' });
});
app.listen(port, () => {
console.log(`Microservice 1 listening at http://localhost:${port}`);
});
// Microservice 2
const express2 = require('express');
const app2 = express2();
const port2 = 3002;
app2.get('/service2', (req, res) => {
res.json({ message: 'Microservice 2 response' });
});
app2.listen(port2, () => {
console.log(`Microservice 2 listening at http://localhost:${port2}`);
});2. Microservices with Koa.js
Koa.js, with its modern and lightweight design, provides an excellent foundation for building microservices. Its use of async/await simplifies handling asynchronous operations. Below is a basic example:
// Microservice 1
const Koa = require('koa');
const app = new Koa();
app.use(async ctx => {
ctx.body = { message: 'Microservice 1 response' };
});
app.listen(3001, () => {
console.log('Microservice 1 listening at http://localhost:3001');
});
// Microservice 2
const Koa2 = require('koa');
const app2 = new Koa2();
app2.use(async ctx => {
ctx.body = { message: 'Microservice 2 response' };
});
app2.listen(3002, () => {
console.log('Microservice 2 listening at http://localhost:3002');
});3. Microservices with Nest.js
Nest.js, with its modular and TypeScript-friendly structure, simplifies building scalable microservices. It provides decorators and a powerful dependency injection system. Here’s a basic example:
// Microservice 1
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
await app.listen(3001);
}
bootstrap();
// Microservice 2
import { NestFactory } from '@nestjs/core';
import { AppModule } from './app.module';
async function bootstrap() {
const app = await NestFactory.create(AppModule);
await app.listen(3002);
}
bootstrap();4. Microservices with Sails.js
Sails.js simplifies building data-driven APIs and real-time applications, making it suitable for microservices. It provides a blueprint API for generating controllers, models, and services. Here’s a basic example:
// Microservice 1
module.exports = {
async find(req, res) {
res.json({ message: 'Microservice 1 response' });
}
};
// Microservice 2
module.exports = {
async find(req, res) {
res.json({ message: 'Microservice 2 response' });
}
};5. Microservices with Adonis.js
Adonis.js, with its full-stack features, simplifies building microservices with built-in ORM and strong conventions. Here’s a basic example:
// Microservice 1
'use strict';
class MicroserviceController {
async index() {
return { message: 'Microservice 1 response' };
}
}
module.exports = MicroserviceController;
// Microservice 2
'use strict';
class MicroserviceController {
async index() {
return { message: 'Microservice 2 response' };
}
}
module.exports = MicroserviceController;
Conclusion
Choosing the right Node.js framework for your microservices depends on your project’s requirements and your development preferences. Whether you prefer a minimalistic approach, a modern JavaScript experience, or a full-stack framework, the frameworks mentioned above cover a spectrum of needs. Explore these frameworks, consider your microservices architecture, and leverage the strengths of these tools to build scalable, modular, and maintainable microservices with Node.js.