Introduction
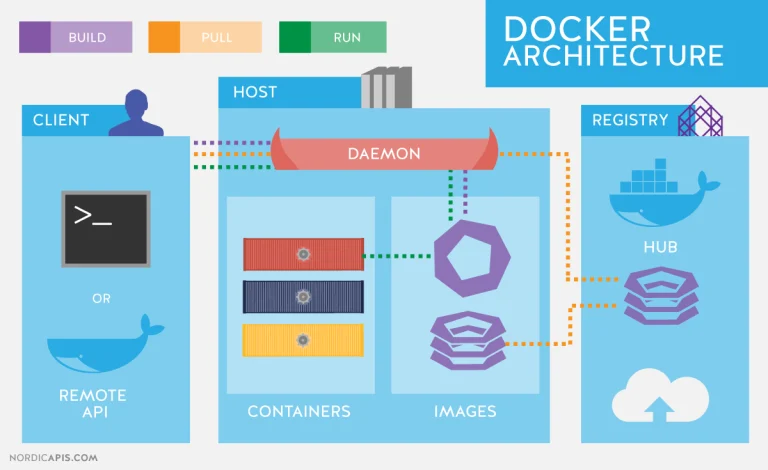
Docker offers a seamless solution for containerizing full-stack web applications. In this article, we’ll guide you through the process of creating Dockerfiles for Apache, PHP, and MySQL, providing a foundation for efficient development, testing, and deployment.
- Choosing Base Images:
Start by selecting suitable base images. For Apache and PHP, use the official images likephp:7.4-apache. For MySQL, choose the official MySQL image. Ensure compatibility between versions to avoid potential issues. - Setting Up Dockerfile for Apache and PHP:
Create a Dockerfile for Apache and PHP, leveraging a multi-stage build for optimization. Install necessary dependencies, enable required Apache modules, and configure the document root.
# Stage 1: Build FROM php:7.4-apache as builder WORKDIR /var/www/html COPY . . # Install dependencies and configure Apache # Stage 2: Production FROM php:7.4-apache WORKDIR /var/www/html COPY --from=builder /var/www/html . # Additional configurations, if needed
- Configuring PHP and Apache:
Adjust PHP and Apache configurations according to your application needs. Enable necessary PHP extensions, configure PHP settings, and set up Apache virtual hosts if you have multiple sites. - Setting Up Dockerfile for MySQL:
Create a Dockerfile for MySQL, specifying the version, creating a database, and configuring user permissions.
FROM mysql:8.0 # Set up MySQL database and user # Additional configurations, if needed
- Docker Compose for Orchestration:
Compose the services using adocker-compose.ymlfile. Define services for Apache, PHP, and MySQL, ensuring they can communicate with each other. Include environment variables for MySQL authentication.
version: '3'
services:
apache-php:
build: .
ports:
- "80:80"
depends_on:
- mysql
mysql:
image: mysql:8.0
environment:
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: root_password
MYSQL_DATABASE: app_db
MYSQL_USER: app_user
MYSQL_PASSWORD: app_password- Connecting PHP to MySQL:
Modify your PHP application’s database configuration to connect to the MySQL service. Use the service name defined in thedocker-compose.ymlfile as the MySQL host. - Building and Running the Docker Containers:
Build and run the Docker containers using thedocker-composecommand. Ensure that the containers start up successfully and can communicate with each other.
docker-compose up -d
- Testing and Debugging:
Test your application within the Docker environment. If issues arise, use Docker logs and inspect commands to identify and debug potential problems. - Optimizing for Production:
Remove unnecessary dependencies, configurations, and debug tools from the production Dockerfile to create a lean and secure image for deployment. - Scaling and Load Balancing (Optional):
If your application requires scaling, consider using Docker Swarm or Kubernetes for orchestration. Integrate load balancing solutions for distributing traffic among multiple instances.
Conclusion
Dockerizing a full-stack web application with Apache, PHP, and MySQL provides a portable and consistent development environment. By following these steps, you can efficiently containerize your application, making it easier to collaborate, deploy, and scale in diverse environments.